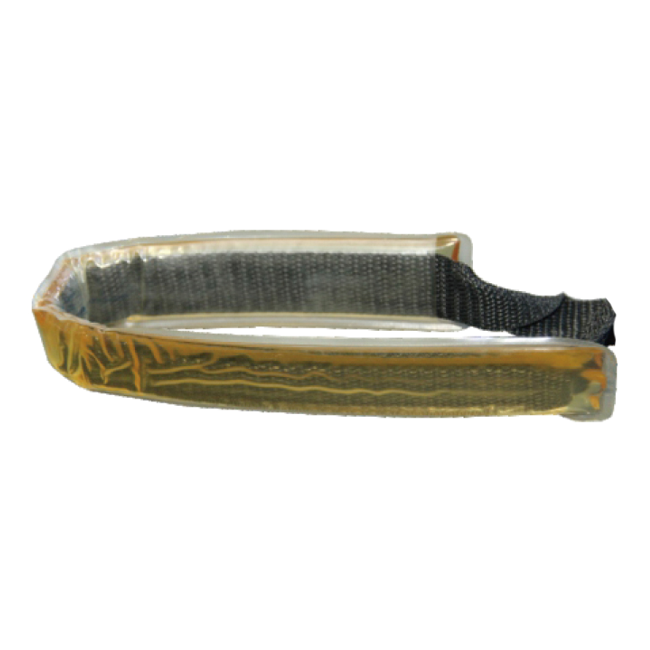
Positioning strap ORP-PS (Fixing Body Strap)
Positioning Strap
Model: ORP-PS-00
Function
1. Minimizing movement on the operating room table
2. Soft, yet strong to ensure proper positioning for security and comfort of extremity
Dimension
50.8 x 9.22x 1cm
Weight
300g
Product parameters
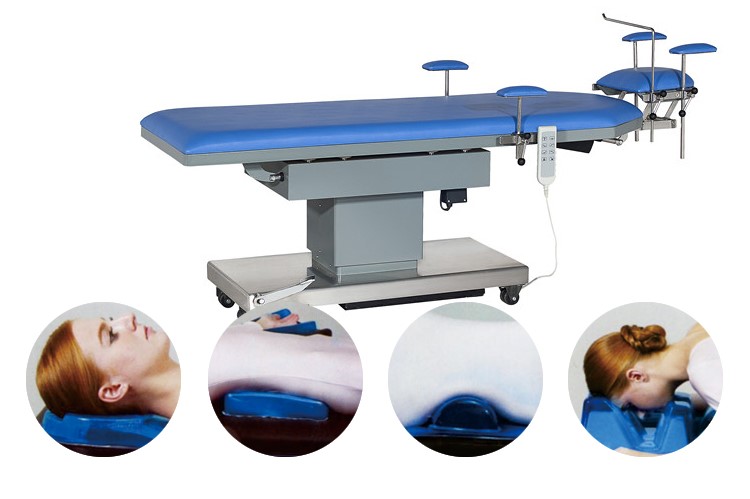
Product Name: Positioner
Material: PU Gel
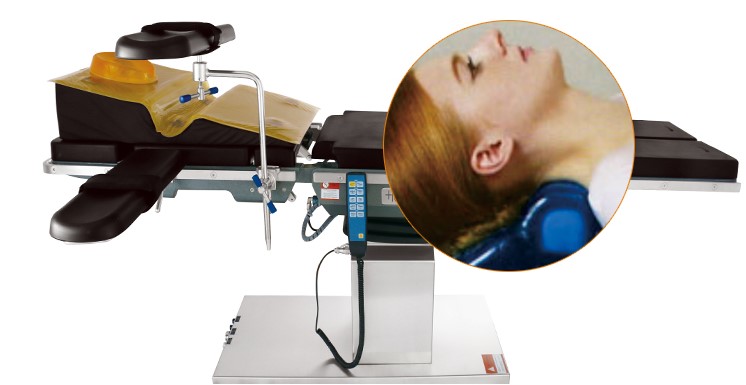
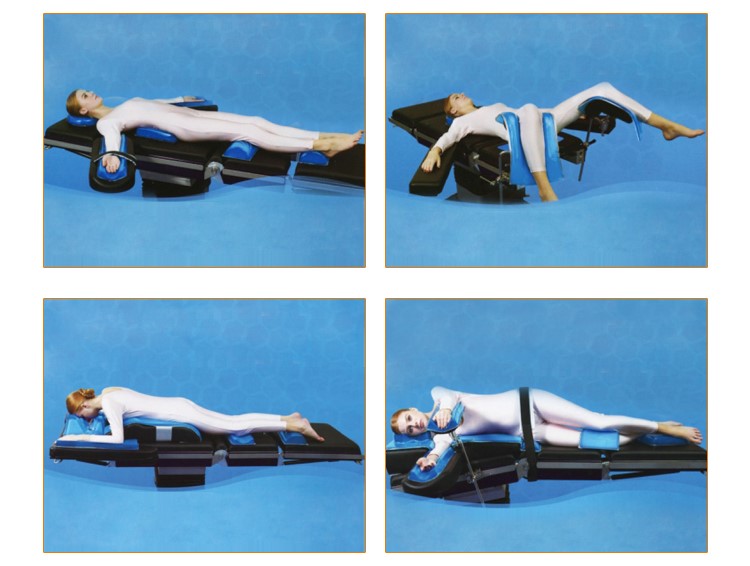
Definition: It is a medical device which is used in an operating room to protect patient from pressure sores during surgery.
Model: Different positioners are used for different surgical positions
Color: Yellow, blue, green. Other colors and sizes can be customized
Product characteristics: Gel is a kind of high molecular material, with good softness, support, shock absorption and compression resistance, good compatibility with human tissues, X-ray transmission, insulation, non-conductive, easy to clean, convenient to disinfect, and does not support bacterial growth.
Function: Avoid pressure ulcer caused by long operation time
Product characteristics
1. The insulation is non-conductive, easy to clean and disinfect. It does not support bacterial growth and has good temperature resistance. The resistance temperature ranges from -10 ℃ to +50 ℃
2. It provides patients with good, comfortable and stable body position fixation. It maximizes the exposure of the surgical field, reduce the operation time, maximize the dispersion of pressure, and reduce the occurrence of pressure ulcer and nerve damage.
Cautions
1. Do not wash the product. If the surface is dirty, wipe the surface with a wet towel. It can also be cleaned with neutral cleaning spray for better effect.
2. After using the product, please clean the surface of the positioners on time to remove dirt, sweat, urine, etc. The fabric can be stored in a dry place after drying in a cool place. After storage, do not put heavy objects on top of the product.
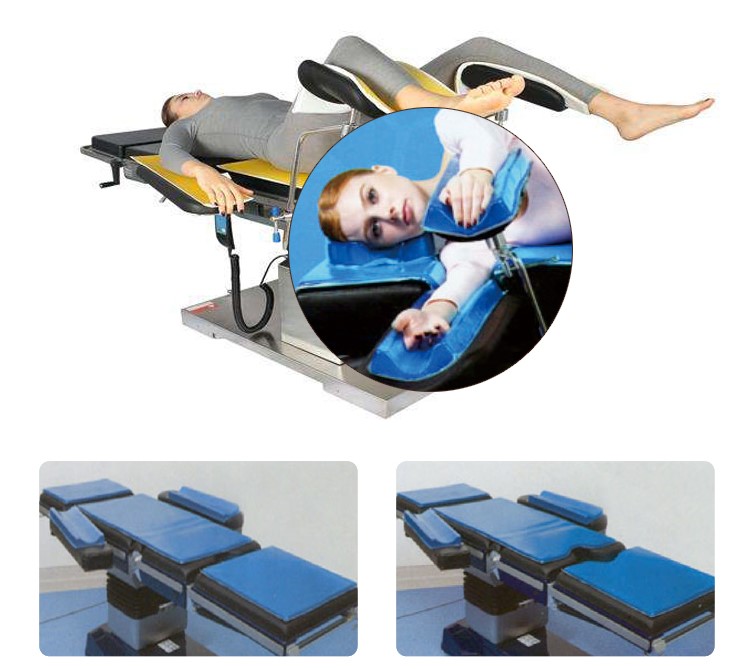
Supine position is the most commonly used surgical position. Positioning strap should be used.
• Common injuries related to the supine position are pressure ulcers on the occiput, scapulae, thoracic vertebrae, elbows, sacrum, and heels
• Arms should either be secured at the sides or extended on arm boards
• Positioning strap should be placed across the thighs, approximately 2 inches above the knees with a sheet or blanket placed between the strap and the patient’s skin. It should not be restrictive to avoid compression and friction injuries
• Patient’s heels should be elevated off the underlying surface when possible
General safety measures for Trendelenburg position:
(1) Brachial plexus injuries are associated with the use of shoulder braces. If possible, avoid the use of shoulder braces; however, if they must be used, the braces should be well-padded. The braces must be placed on the outer parts of the shoulder away from the neck.
(2) The safety strap should be placed 2” above the knees. It should not be restrictive to avoid compression and friction injuries.
(3) The operating room table should be adjusted into the head downward position slowly to allow the physiological processes of the patient’s body to adjust, as well as leveled slowly at the end of the surgical procedure. Trendelenburg’s position increases the intracerebral and intraocular pressures. If it can be avoided, patients who have a history of head trauma or intracranial pathology should not be placed in Trendelenburg’s position.
Cardiovascular changes are seen with Trendelenburg’s position. If it can be avoided, patients who have a history of cardiovascular pathologies including heart failure and myocardial infarction as well as peripheral vascular disease that interferes with venous return, should not be placed in Trendelenburg’s position.
Diaphragmatic movement is impaired by the weight of the abdominal viscera. The combined pressure of the viscera and increased airway pressure to ventilate the lungs,
which causes the diaphragm to push back against the viscera, increases the risk for atelectasis.
(4) When tilting the bed head downward, the surgical team should closely observe the patient to prevent sliding and causing a shear injury and/or falling off the OR table.
Remarks: The Operating Room table safety positioning strap must not be secured too tightly across the patient in order to avoid pressure that can compromise circulation and friction. The surgical technologist should be able to comfortably insert two fingers under the mid-section of the safety strap to assure it is safely applied.








